Career Pathways, Job Roles, and CPD/Qualification Support
The education data profession is at a crossroads. While the importance of data in driving school improvement is widely recognised, there remains a gap in understanding and resourcing the profession effectively. This is where Workstream 2 comes in—a comprehensive exploration of career progression, roles, and skillsets within the education data landscape.
It’s important to clarify that while the main output of this workstream outlines various roles, it doesn’t imply that trusts require all 33 positions. Rather, it serves as a roadmap, indicating roles that should be encompassed within trust staffing structures but outlines that the necessity for these roles depends on the maturity of data systems within a trust. For example, employing someone to oversee data science may not be prudent in the early stages of a trust’s data maturity journey. Additionally, certain elements can be outsourced, which is often economically sensible, especially for smaller trusts. For instance, the data engineering pathway can be addressed through Management Information Systems (MIS) and other educational technology (Edtech) avenues.
This document aims to empower executive members and data professionals alike to construct or develop finely tuned teams tailored to organisational needs, ensuring maximum efficiency and effectiveness in data management and analysis. For data professionals seeking career advancement, this guide provides valuable insights into developing their own career paths within the sector. Act now to explore the possibilities and pave the way for strategic growth and adaptation in the ever-evolving data landscape.
Career Pathways Overview
Within education data management, five distinct career pathways have been identified, each comprising specialised roles that contribute to the effective utilisation of data in educational settings. These pathways include Data Compliance and Governance, Information Systems and Quality, Data Analytics, Data Engineering, and Information Strategy. It’s crucial to understand that these roles are often combined within job descriptions in many trusts, reflecting the multifaceted nature of data management within educational institutions. While the size of data teams may vary based on trust/school maturity, the roles outlined in the career progression map are essential components of a well-rounded data strategy.
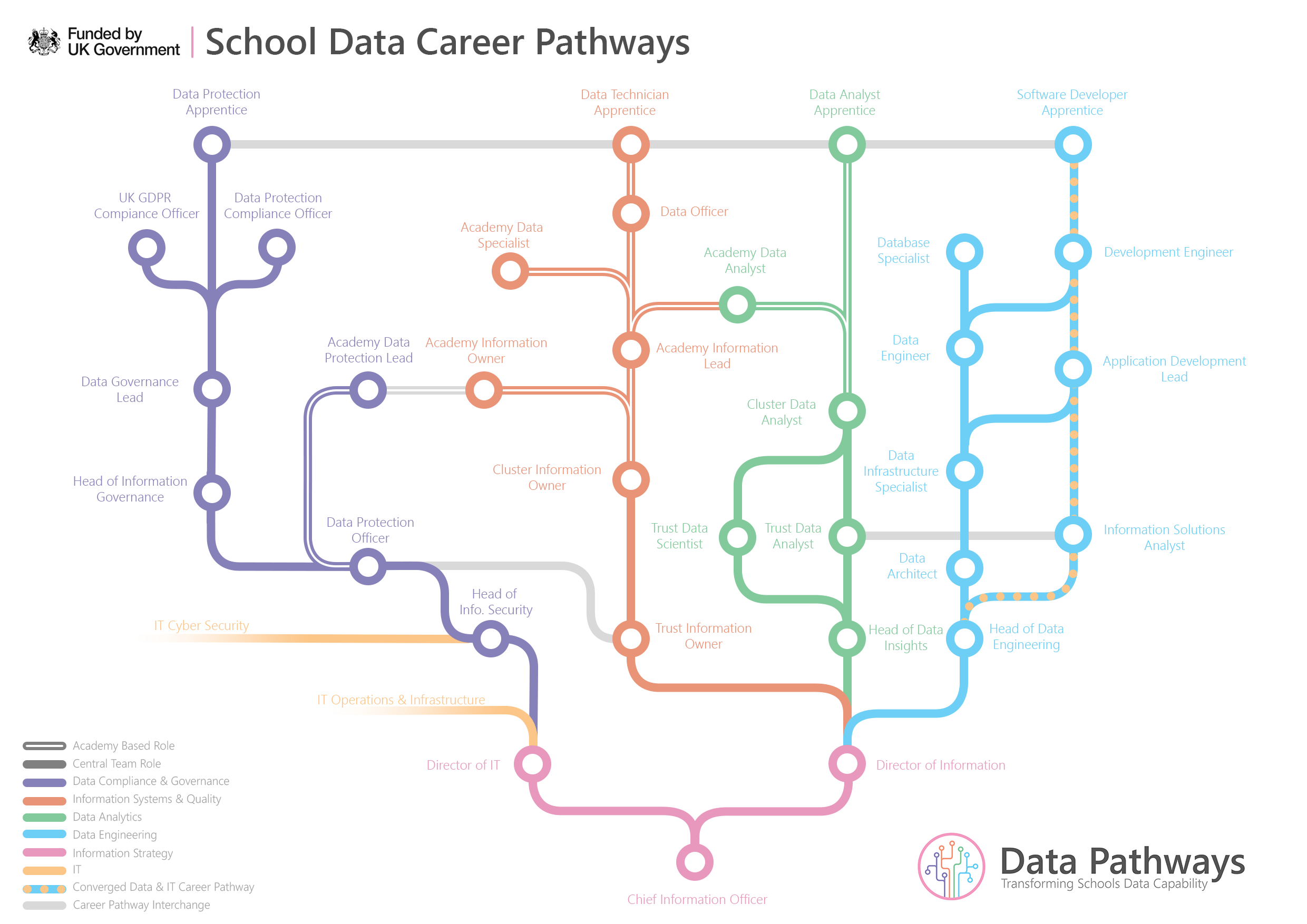
Integration of Career Pathways
While each career pathway offers unique opportunities for specialisation, collaboration between professionals across different pathways is essential for maximising the impact of data within educational organisations. By leveraging the diverse skill sets and perspectives offered by each pathway, educational institutions can effectively address complex data challenges and achieve their strategic objectives.
Interactive Career Roles
Discover the world of data roles and unlock your potential in the dynamic field of data technology and analytics. Click through to explore an interactive career role map and delve into comprehensive role descriptions that will empower you to chart your path in the data industry.
Job Role Portfolio Document
As part of our initiative to enhance career pathways and provide clarity on job roles within education data management, we have produced a comprehensive Job Role Portfolio document. This document serves as a valuable resource for educational institutions, offering detailed descriptions of various data-related roles and outlining the specialist skills, soft skills, qualifications, and salary expectations associated with each role.
Role Descriptions
Empower yourself with the understanding of diverse data roles to navigate the evolving landscape of data technology and analytics.
Placement of Data Roles: MAT Operations vs. Education
The placement of data management roles within a MAT presents a strategic decision with implications for organisational effectiveness and alignment. Centralising data roles within MAT Operations offers several advantages. Firstly, it streamlines data functions, leading to greater efficiency and consistency in data management practices. This approach also facilitates the implementation of standardised processes and protocols for data governance, ensuring uniformity across all schools within the trust. Additionally, by consolidating data functions, MAT Operations can optimise resource allocation and minimise duplication of efforts, resulting in cost savings and improved operational efficiency. Moreover, housing data roles within MAT Operations encourages collaboration and knowledge sharing among data professionals, fostering a cohesive and supportive working environment.
On the other hand, embedding data roles within the education department of a MAT also offers unique benefits. Placing data roles within the education department ensures closer alignment with teaching and learning objectives, enabling data professionals to directly contribute to educational outcomes and student success. This approach promotes collaboration between data professionals and educators, facilitating the integration of data-driven insights into pedagogical practices and decision-making processes. Additionally, data professionals working within the education department are better positioned to understand the specific needs and priorities of educators, allowing for tailored support and solutions. However, this approach may introduce challenges related to data governance, particularly in ensuring consistency and compliance with data policies and regulations across decentralised school structures. Moreover, managing data functions within the education department of a MAT may require greater coordination and communication to ensure coherence and alignment of data practices across various schools and departments.